Left Join Query In Laravel 9 Example
In this article, we will see the left join query in the laravel 9 examples. laravel 9 left join eloquent returns all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table, The result is NULL from the right side. We will also see the left join with groupBy() in laravel 9. If you would like to perform a "left join" or "right join" instead of an "inner join", use the leftJoin or rightJoin methods. These methods have the same signature as the join method.
So, let's see examples of laravel 9 left join query, join query in laravel 9, left join in laravel 9, laravel 9 join two tables, laravel 9 left join group by, laravel left join subquery, left join query in MySQL.
For the laravel 9 left join query example we need the first argument passed to the leftJoin method to be the name of the table you need to join to, while the remaining arguments specify the column constraints for the join. Left join query use in laravel 6, laravel 7, laravel 8, and laravel 9.
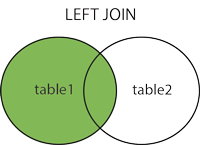
In this example, we will create users table and countries table. we will add the country_id foreign key to the user's table. So, when I get users at that time we will get the country name from country_id using left join.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all records from the left table (table1), and the matching records from the right table (table2). The result is 0 records from the right side if there is no match.
select `users`.`id`, `users`.`name`, `users`.`email`, `countries`.`name` as `country_name`
from `users`
left join `countries` on `countries`.`id` = `users`.`country_id`
In this example, select data like id, name email, and country name but if you want all fields then you can use * to select all data.
public function index()
{
$users = User::select('users.id', 'users.name', 'users.email', 'countries.name as country_name')
->leftJoin('countries', 'countries.id', '=', 'users.country_id')
->get();
}
Using DB:
$users = DB::table('users')
->leftJoin('posts', 'users.id', '=', 'posts.user_id')
->get();
$users = DB::table('users')
->rightJoin('posts', 'users.id', '=', 'posts.user_id')
->get();
Now, we will give an example of a multiple where conditions with an aggregate function.
User::leftJoin('posts', 'users.id', '=', 'posts.user_id')
->select('users.*')
->where('is_published', true)
->where('views','>=','100')
->get();
You might also like:
- Read Also: How To Get Current Month Records In MySQL Query
- Read Also: How To Import CSV File In MySQL Using Node.js
- Read Also: Laravel 8 One To Many Relationship Example
- Read Also: Laravel REST API CRUD Tutorial